
Crypto Scams: What They Are & How To Avoid Them
As cryptocurrency has grown popularity, so has the frequency of crypto related scams. According to a report by Chainalysis, illicit cryptocurrency transactions equaled $14 billion U.S. for 2021. This figure is expected to be larger for 2021.
Crypto scams come in different forms and use various tactics. And with the increased frequency of crypto attacks, it’s perfectly normal to feel anxious about crypto trading. However, we are here to help. This article will cover some of the common cryptocurrency scams. There will also be sections on how to identify cryptocurrency scams, how to avoid them, and what to do if you have fallen victim to one. So, let’s get started with some of the most prevalent cryptocurrency scams.
Common crypto scams
Phishing scams
Phishing scams are a commonplace internet attack used in various industries. In the crypto world, phishing scams usually target crypto wallets. The goal of the scammer is to gain access to your crypto wallet and drain the funds from it. They are usually delivered by text or email but can also come through messaging apps (e.g, Facebook Messanger) or by phone. A phishing scam will appear to be from a legitimate sender, like your bank or cryptocurrency exchange. The message will ask you to reveal personal information about your crypto wallet, like the address or password/pin number.
Phishing scams have several identifiable characteristics. They include:
- Creating a sense of urgency
- Offering gifts or incentives
- Containing fraudulent links or attachments
For example, you may receive an email from your cryptocurrency exchange warning you that your account has been hacked and that you must sign in and update your settings. The message will prompt you to click the attached link to log in. However, the link will actually send you to a fraudulent website the scammer has set up. Once you sign in and update your personal info, the scammer will take that information to hack your actual account and steal your crypto.
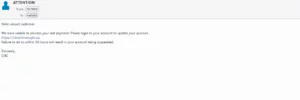
An example of a phishing email.
Click the link here to learn more about phishing scams. Click here to learn how to spot phishing attacks.
Crypto investment scams
This is a broader category as these scams can come in various forms.
ICOs stands for initial coin offerings. These occur when a new cryptocurrency is released. ICOs are popular with investors because it gives them a chance to buy a coin at a relatively low price before it explodes in popularity. However, ICOs have a high potential for scams. A scammer will claim to have created a new cryptocurrency that will soon become popular. They will encourage people to invest in the coin, assuring them that the coin will soon be worth thousands of dollars. In reality, the coin does not exist, and the scammer will disappear once they have stolen enough money. A recent example of an ICO scam is the Squid crypto collapse. In late October 2021, a new cryptocurrency called Squid was launched, the coin was based on the Netflix series Squid Game. The coin was instantly popular, and by early November Squid’s price reached $2,860 U.S. However, Squid’s unknown developers suddenly cashed out around $3,000,000 worth of Squid. Investors in the token lost thousands of dollars.
Pump and dump schemes have existed for many years, and they have made their way into the crypto world. This scam involves an individual or organization encouraging people to invest in a cryptocurrency through false/misleading claims (“This coin will be the next big thing”). As more people invest in the cryptocurrency, its price will steadily rice. Once the price hits its peak, the scheme operators will sell their shares of the coin. The price will fall, and all those who invested in the coin will lose their money.
The decentralized nature of cryptocurrency has spawned a scam called DeFi Rug Pulls. DeFi stands for deregulated finance, meaning there is no regulating body. DeFi Rug Pulls set up fake protocols which appear to support an online marketplace that supports unregulated transactions. The scammer will get people to invest in the protocol. Once they have stolen enough money, they will quickly shut down the protocol.
Fake websites and exchanges
These are fraudulent sites that claim to be a place where you can buy cryptocurrency. In reality, a scammer has set up the site to steal people’s money. To fool people, the fraudulent site mimics a legitimate crypto site. For example, the domain name will be similar but have slight differences.
Fraudulent crypto exchanges use various tactics to steal your money. You may be able to make a few small withdrawals from the site. But once you invest more money into the webpage, your will be unable to make withdraws. The site will claim there was an issue with the payment, or it will suddenly shut down.
Digital collectibles and games
Cryptocurrency has spawned various related games and digital collectibles. Scammers will develop a fake game or digital collectible that is related in some way to cryptocurrency. For games, users are typically told that they could earn free crypto if the buy and play they game. Digital collectibles are usually NFTs. Scammers will create a fake NFT and encourage people to buy it using cryptocurrency. Once they receive your crypto, the scammer will not send over the NFT and will cut off contact with you.
Imposter scams
These scams involve someone posing as a celebrity, business figure, or a crypto related influencer. The imposter will encourage people to buy a particular coin, or they will promote a specific currency or crypto-related product. Often times the promoted coin or crypto product is fake; it is set up by a scammer to steal money. A recent example of an imposter scam involves Tesla CEO Elon Musk. The scam used a deepfake video of Elon Musk telling people to invest in an unauthorized crypto exchange. Musk promptly tweeted that the video was not real. Even though the Elon Musk deepfake was quickly debunked, there are plenty of complex and convincing imposter scams out there.
The Elon Musk deepfake video, reported by twitter user DogeDesigner
Giveaway scams
Giveaway scams are fairly simple. A scammer promises to match or multiply the amount of crypto send to them. For example, if you sent the scammer 12 Bitcoin, they will send you either an equal or greater amount of Bitcoin in return. While this may seem like an obvious scam to point out, clever and convincing wording can trick some people. Other times, the scammer will use a legit-looking website to pull of their giveaway scam.
Romance scams
If you use dating apps like Tinder or Bumble, you may come across a romance scam. This scam involves one person pressuring their match to send them crypto or send them money to buy crypto. The scammer and their victim usually do not meet; the relationship will be entirely digital.
Cloud mining scams
Cloud mining is a service in which a company operates crypto mini hardware and charges a fixed fee to rent the hardware. This service is designed to simplify the mining process. Most cloud mining companies attract customers with enticing offers such as low fees, sign-up bonuses, and large earnings. However, some of these companies are completely fake and are designed to steal your money. Other cloud mining companies are legitimate, but the service they provide is largely ineffective. This means you end up paying an expensive fee to use the company’s mining hardware while earning very little cryptocurrency in return.
Blackmail/extortion scams
Blackmail and extortion scams are another popular method scammers use to steal your money. They send an email claiming to have a record of you visiting an adult website or other illegal web pages. Other times, the scammer claims to have videos of you in compromising situations. The scammer will threaten to reveal this information unless you send them cryptocurrency or the private key to your crypto wallet. Most of the claims have no basis behind them, but you should report these messages to law enforcement; blackmail and extortion is illegal in Canada.
How to identify cryptocurrency scams
Now that we have covered some common cryptocurrency scams, let’s look at how you can spot them. While each scam has their own wording or strategies, there are some shared characteristics between them.
Guaranteed returns
Many crypto scams will promise that you will get a 100% return on your investment. Other scams will assure you that their product is guaranteed to make you money. If you see these claims in any offer, it is a definite red flag.
Free money
This characteristic relates to the previous one. A scam will claim that you will receive free crypto or cash with no strings attached. While most legitimate exchanges offer free crypto, you have to perform a task to earn it; for example, referring your friend to the exchange. Be wary if you are offered free crypto/cash without having to perform a specific task.
Poor/fake whitepaper
A whitepaper is used by developers to explain the project they are working on and how it works. Crypto developers use whitepapers to explain the information behind the coin they are releasing. They usually contain statistics, diagrams, and formulas about the cryptocurrency. The goal of the whitepaper is to get people to invest in the currency. Any legitimate cryptocurrency should have whitepaper.
Fraudulent cryptocurrencies often have poorly written whitepapers. The information will be confusing, and the document usually has numerous spelling and grammatical errors. Sometimes the whitepaper does not exist.
Unknown developers
Every legitimate cryptocurrency and crypto related service has a group of developers behind it. It should be easy to find background info on each person, such as their education and past projects. Each member usually has an active social media presence. If you are having a hard time finding who is behind a cryptocurrency or crypto relate product, be cautious. While not every legit crypto developer will have an active social media presence, scammers take extra measures in order to hide their identity.
Overdone marketing
In order to reach a larger demographic, scammers will put a lot of effort into marketing. You will likely see well produced videos and slickly designed online ads. This makes it hard to determine whether the ads are for a legitimate or fraudulent crypto coin or service. One trait of fraudulent crypto marketing is extravagant claims. For example, “Invest in this cryptocurrency and earn up to $10,000 in return”. The wording in these ads tend to be heavy-handed, in other words excessive. In any case, do some research into the product being advertised.
Protecting yourself from crypto scams
There are several things you can do to protect yourself from crypto scams.
It is always important to do some research before you begin crypto trading. I recommend that beginners read some articles and watch a few videos on cryptocurrency to become familiar with the terminology, theory, and investing strategies. If you are interested in buying a new coin, research its developers and see if you can read its whitepaper. Try and find reviews from trusted individuals and websites. You can also find webpages that list fake cryptocurrencies and fake crypto web sites. TrendMicro has a list of fraudulent crypto webpages, which is updated regularly.
Crypto wallets are arguably the most important part of crypto trading. Without one, you stand a higher chance of having your crypto assets stolen. Because of their importance, you should ensure your wallet is safe from scams. Never divulge your private keys to anyone. If a website asks for your private keys, then it is a scam. Set up security features like multifactor authentication and recovery phrases; this makes it harder for scammers to access your wallet.
Lastly, be wary of social media posts advertising crypto coins and related products. Scammers will often use unauthorized images of celebrities or notable people to promote their scheme. This creates a sense of legitimacy. While some of these adverts are legitimate, it’s always best to be cautious when you see them. Always do your research into crypto social media posts to gauge their legitimacy.
These are just a few examples of ways you can protect yourself from crypto scams. To see more steps you can take, check out this article.
Frequently asked questions about crypto scams
What do I do if I have fallen to a crypto scam?
Falling victim to a crypto scam is a horrible experience. While you will feel anxious, try your best to be level-headed. Take a moment to collect your thoughts. Next, gather all the information related to the fraud, which may include documents, screenshots of emails or texts, and receipts.
Once you have gathered your information, contact your bank. Let them know of the crypto scam and, depending on the situation, you may have to cancel your debit/credit card. If your crypto wallet is compromised, contact your wallet provider. They will walk you through the next steps. If a scam occurs on a cryptocurrency exchange, report it to the site’s administrators.
You can also contact your local police to report the incident. They will keep a file on hand for future reference. Lastly, report the scam to the relevant anti-fraud organization. For Canadians, that would be the Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre.
Because of the decentralized nature of the blockchain, any crypto transaction can be traced. Therefore, you can have a governing body access the blockchain and track your stolen crypto to wallet it was sent to. You may end up getting some back.
What are some NFT scams?
NFTs have many of the same scams as cryptocurrency. Rug pulls, phishing messages, and pump and dump schemes are some of the common NFT scams. One scam that is unique to NFTs is plagiarised content and art theft. Scammer will illegally download digital art and sell them as NFTs; they will claim they created the art.
DevianArt, a digital art website, has a tool called DevianArt Protect to protect users from art theft. The tool scans blockchains to find stolen artwork. The artist is then alerted to the theft. DevianArt Protect will also scan DevianArt itself for any possible threats. The downside to this tool is that it will not automatically take down the stolen art. It is up to the individual artist to contact DevianArt or the NFT marketplace to have the plagiarised art removed.

An example of a verified NFT seller. Source: OpenSea
There are some things you can do to prevent NFT theft. First, make sure the seller’s account is verified. On the NFT marketplace OpenSea, verified accounts will have a blue check. Check out the seller’s social media accounts to see their activity. You can also track their history on NFT marketplaces. If anything unusual comes up, they are probably a scammer. To check the authenticity of the art, do a Google reverse image search. Doing this will reveal whether the image is original or a copy. Lastly, if you suspect an NFT has been plagiarized, report the seller to the exchange.
Sources used for this article
Kaspersky: Common cryptocurrency scams and how to avoid them
Investopedia: Beware of cryptocurrency scams
NextAdvisor: 6 common crypto scams, and how investors can protect their coins
Read more

What is Blockchain, and How Does it Work?
Blockchain is the backbone of cryptocurrencies. To find out more about this technology, check out this article on blockchain.

Coinbase Review: Features, Trading, Pros and Cons
Want to learn more about Coinbase? Then this is the review for you.

The Best Cryptocurrency Exchanges in Canada
Binance, Bitbuy, BitTrex and more: check the top crypto exchanges in Canada.

What are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are a growing part of the crypto market. This article will look at what stablecoins are and why they are worth buying.